Overview of Ant Dietary Habits
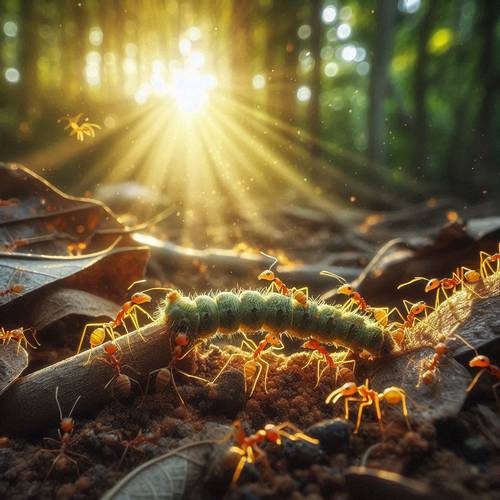
Ants have diverse dietary habits that vary by species and environment. Most ants are omnivores, eating a mix of plant and animal matter. Common foods include nectar, seeds, fungi, and dead insects. Some ants, like leafcutter ants, harvest leaves to cultivate fungus, their primary food source.
Others, such as carpenter ants, prefer sugary substances like honeydew produced by aphids. Predatory ants hunt live prey, including other insects and small animals. This versatility in diet helps ants adapt to various habitats and ensures their survival in different ecological niches.
Others, such as carpenter ants, prefer sugary substances like honeydew produced by aphids. Predatory ants hunt live prey, including other insects and small animals. This versatility in diet helps ants adapt to various habitats and ensures their survival in different ecological niches.
Importance of Insect Consumption for Ants
Insect consumption is crucial for ants, providing essential nutrients needed for their growth, development, and survival. By eating insects, ants obtain proteins, fats, and other vital nutrients that are not always available from plant-based foods. Predatory ants rely heavily on insects as a primary food source, while even omnivorous ants supplement their diet with insects.
This practice not only supports the colony's health but also helps regulate insect populations in their ecosystem. Insect consumption enables ants to fulfill their roles as effective hunters and scavengers, maintaining the ecological balance within their habitats.
This practice not only supports the colony's health but also helps regulate insect populations in their ecosystem. Insect consumption enables ants to fulfill their roles as effective hunters and scavengers, maintaining the ecological balance within their habitats.