Grains and Cereals
Grains and cereals are a staple in a pig’s diet, providing essential carbohydrates and energy. Common grains like corn, barley, and wheat are popular choices. These grains not only help in maintaining energy levels but also support healthy growth and development. Including a variety of grains ensures pigs receive a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Always ensure the grains are clean and free from mold to keep your pigs healthy and thriving.
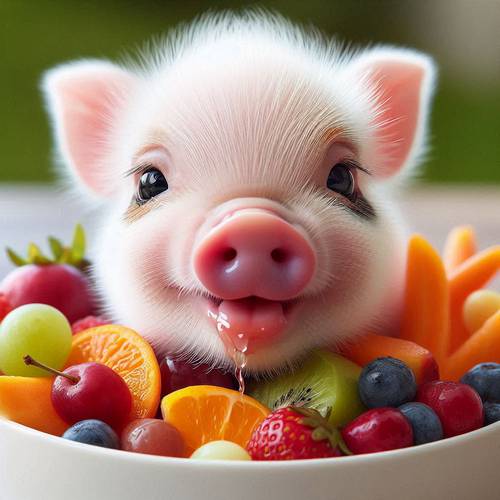
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are essential of a pig's diet, providing vital nutrients and variety. Pigs enjoy apples, pears, and melons, which are rich in vitamins. Vegetables like carrots, pumpkins, and leafy greens offer fiber and essential minerals. These foods contribute to a balanced diet, supporting overall health and well-being. Always ensure fruits and vegetables are fresh and clean to avoid any potential health issues.
Protein Sources
Protein is important in a pig's diet for growth and muscle development. Common protein sources for pigs include soybean meal, which is rich in amino acids, fish meal, providing high-quality protein, and legumes like peas and beans. These sources ensure pigs get the necessary nutrients for optimal health and productivity. Including a variety of protein sources can help balance their diet and support their overall well-being.