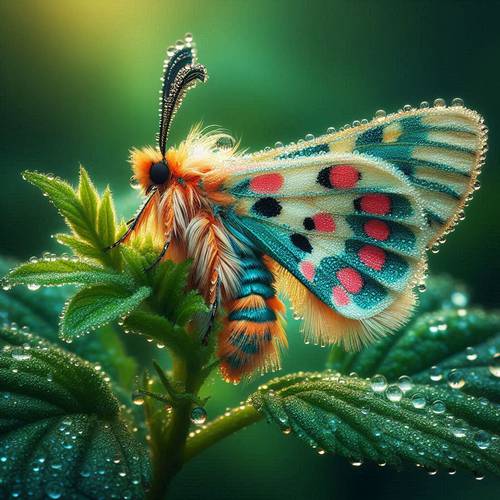
Herbivorous Nature: Exploring Moths' Plant-Based Diet
Moths exhibit a fascinating herbivorous nature, primarily relying on a plant-based diet for sustenance. Their dietary preferences revolve around key plant resources such as nectar, pollen, and various plant parts. Nectar, a sweet liquid found in flowers, serves as a vital energy source for moths, while also providing essential carbohydrates. Pollen grains, often collected inadvertently while feeding on nectar, supplement their diet with proteins and fats.
Additionally, moths consume different plant parts like leaves, stems, and fruits, depending on their species and life stage. This plant-based diet not only nourishes moths but also plays a crucial role in pollination and ecosystem balance, highlighting the intricate relationship between moths and plants in natural environments.
Additionally, moths consume different plant parts like leaves, stems, and fruits, depending on their species and life stage. This plant-based diet not only nourishes moths but also plays a crucial role in pollination and ecosystem balance, highlighting the intricate relationship between moths and plants in natural environments.