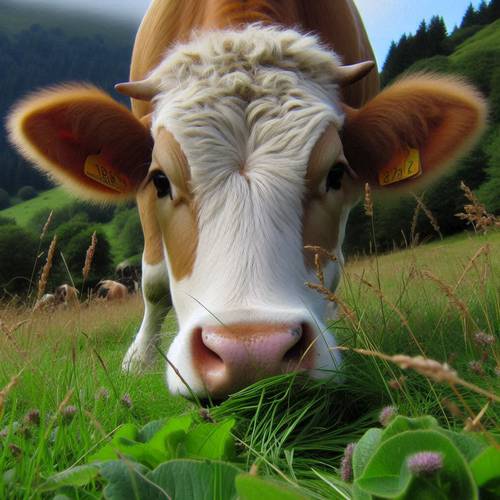
Grasses and Legumes
Cows thrive on a natural diet rich in grasses and legumes. These foods provide essential nutrients, including fiber, protein, and various vitamins, supporting overall health and milk production. Grasses like clover and timothy hay are particularly favored for their high nutritional value.
Legumes offer additional protein and minerals. This balanced diet ensures cows maintain a healthy digestive system and optimal energy levels. Providing access to fresh, high-quality grasses and legumes is crucial for the well-being of both dairy and beef cows.
Legumes offer additional protein and minerals. This balanced diet ensures cows maintain a healthy digestive system and optimal energy levels. Providing access to fresh, high-quality grasses and legumes is crucial for the well-being of both dairy and beef cows.
Hay and Alfalfa
Hay and alfalfa are also staple components of their diet, especially during winter or when fresh pasture isn't available. These dried forages provide essential fiber and nutrients, promoting digestive health and overall well-being. Alfalfa, in particular, is rich in protein, making it a valuable feed for lactating cows. Ensuring access to these natural foods helps maintain healthy, productive cattle.
Fruits and Vegetables
A cow's natural diet includes a variety of fruits and vegetables that provide essential vitamins and minerals. They enjoy munching on apples, pumpkins, and carrots, which add flavor and nutrients to their meals. These foods are excellent supplements to their primary diet of grasses and legumes, helping maintain their health and productivity. Including fruits and vegetables in a cow's diet supports their immune system, promotes good digestion, and enhances overall well-being, making them a vital part of a balanced and nutritious diet.